The United States military is a formidable institution, tasked with safeguarding national security and advancing the country’s interests both domestically and abroad. Its presence spans various branches, including:
- Army
- Navy
- Air Force
- Marine Corps
- Coast Guard
- Space Force
While its size and composition have evolved over the years in response to global conflicts, technological advancements, and strategic needs, the US military continues to play a vital role in the geopolitical landscape.
Its capacity to maintain readiness for both present and future challenges is shaped by the diverse makeup of its personnel, which includes active-duty members, reservists, and civilian support staff.
But what is the actual size of the US military?
Let us talk about it.
Table of Contents
ToggleTotal Military Size in 2025
As of 2025, the US military is composed of approximately 1,130,451 active-duty personnel, according to DMDC.
- Army: 385,252 personnel
- Navy: 292,215 personnel
- Air Force: 258,847 personnel
- Marine Corps: 145,804 personnel
- Space Force: 9,133 personnel
- Coast Guard: 39,200 personnel
In addition to the active-duty personnel, the military is supported by:
- Reserves and National Guard: Approximately 736,050 members
- Civilian employees (Department of Defense): Around 754,000
When combining active-duty personnel, reserves, and civilians, the total military force amounts to roughly 2.6 million individuals.
While this total reflects the broad scope of the military’s operations and responsibilities, it also represents a smaller force compared to historical peaks.
The decline in active-duty personnel is largely due to ongoing recruitment challenges and other factors that will be explored further.
Interesting Fact: Only India (1.4 million) and China (2.0 million) have more active-duty personnel than the US, according to Statista.
The Number of Active Soldiers per State
Now that we know the number of active personnel in the US Army, let us see their distribution by region, as presented by Visual Capitalist:
West Coast
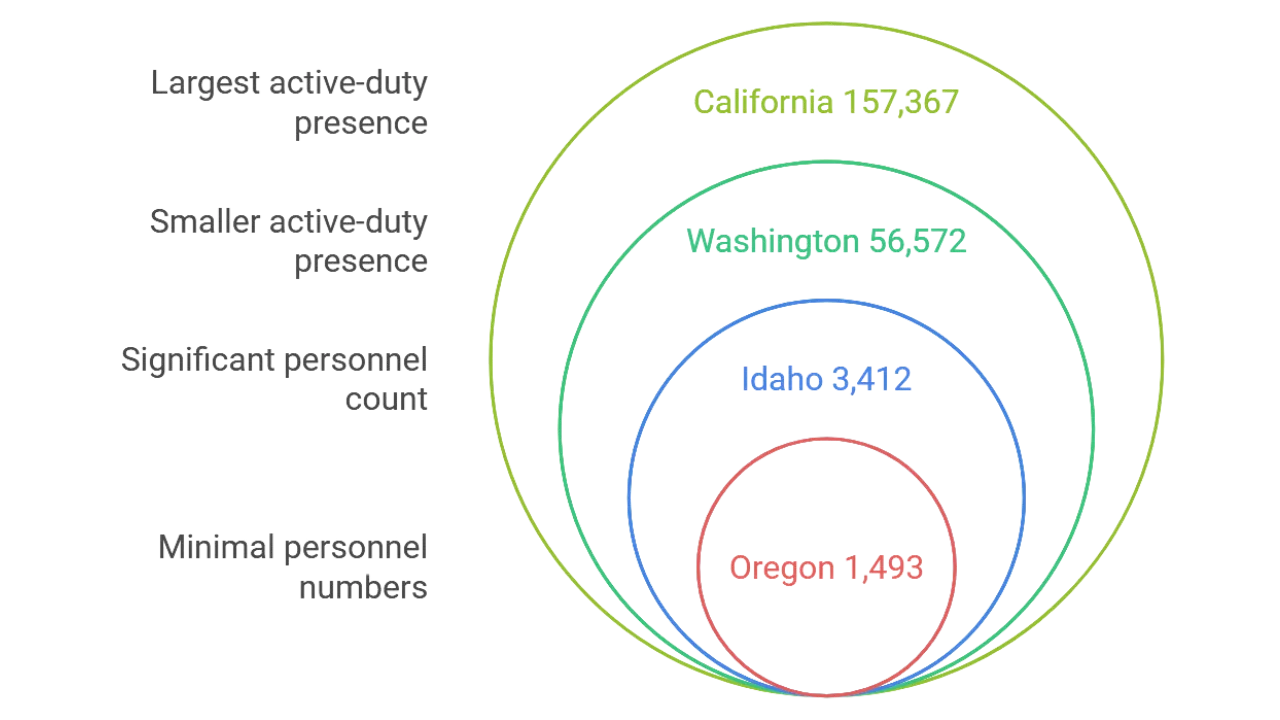
The West Coast hosts a significant number of active-duty personnel, largely driven by California’s numerous bases and strategic ports.
- California: 157,367 active-duty personnel, ranked 1st in the nation.
- Washington: 56,572 active-duty personnel
- Idaho: 3,412 active-duty personnel
- Oregon: 1,493 active-duty personnel
California’s coastal location and international port access make it a key hub for military activity, particularly in the Navy and Marine Corps. Washington also stands out due to its naval installations and proximity to the Pacific.
Midwest and Central States
The Midwest and Central states show varied distribution, with a few states like Texas, Kentucky, and Colorado hosting large numbers, while others have relatively few personnel.
- Texas: 111,005 active-duty personnel
- Kentucky: 30,755 active-duty personnel
- Oklahoma: 19,084 active-duty personnel
- Kansas: 19,769 active-duty personnel
- Illinois: 17,197 active-duty personnel
- Ohio: 6,694 active-duty personnel
States like Texas and Kentucky are home to some of the largest Army and Air Force installations, while other central states support specific bases with more specialized missions.
East Coast
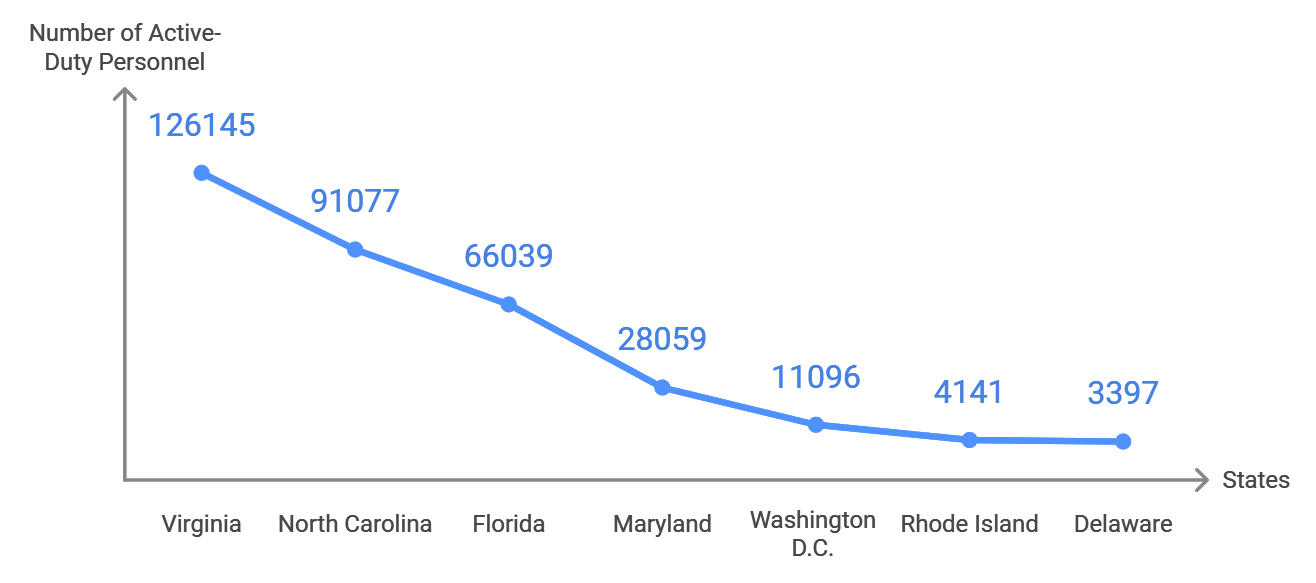
The East Coast is another focal point for military personnel, with Virginia and North Carolina leading due to major Army, Navy, and Marine bases.
- Virginia: 126,145 active-duty personnel
- North Carolina: 91,077 active-duty personnel
- Florida: 66,039 active-duty personnel
- Maryland: 28,059 active-duty personnel
- Washington D.C.: 11,096 active-duty personnel
- Rhode Island: 4,141 active-duty personnel, ranked
- Delaware: 3,397 active-duty personnel
With proximity to the nation’s capital and the Atlantic Ocean, these states house diverse branches of the military, including substantial naval and Marine Corps forces.
Smaller Military Presence
Several states have minimal active-duty personnel, often due to a lack of large military installations. These states include:
- Maine: 824 active-duty personnel
- Minnesota: 567 active-duty personnel
- Iowa: 202 active-duty personnel
- West Virginia: 183 active-duty personnel
- Vermont: 125 active-duty personnel
Interesting Fact: The biggest US Military base on the American soil is Fort Liberty, located in North Carolina.
Comparison to Historical Size and Strength

The size of the US military in 2025 reveals a sharp decline compared to its historical peaks.
- World War II Peak (1945): The US military reached an all-time high with 12.2 million active-duty personnel.
- Vietnam War Era (1968): It had 3.5 million active-duty members.
However, in 2025, the military has shrunk considerably, with only 1.3 million active-duty personnel, marking the smallest force since pre-World War II levels, when there were only 458,365 personnel in 1940.
Recent trends reflect a continued reduction:
As FoxNews writes, in the past three years, the military has lost 64,000 personnel, exacerbating its decline.
Despite technological advancements such as the increased use of drones, artificial intelligence, and cyber warfare, this smaller force brings challenges.
The shrinking number of troops reflects shifting priorities and recruitment struggles, raising concerns about the US’s ability to:
- Project global power effectively.
- Respond to international crises as it did during previous military high points.
Interesting Fact: The US army, like other NATO armies, uses NATO Phonetic Alphabet for communication.
Factors Influencing the Shrinkage
In fiscal year 2023, the military fell short of its recruitment goals by an astonishing 41,000 personnel, deepening the ongoing reduction in force size and compounding the challenges of maintaining a robust military presence.
Several factors have contributed to the reduction in military personnel in 2025:
| Factor | Summary |
|---|---|
| Economic Opportunities | Strong economy offers alternative career paths, reducing military appeal. |
| Institutional Trust | Gen Z’s institutional distrust decreases interest in military service. |
| Qualification Challenges | Fewer applicants meet fitness, education, and eligibility requirements. |
| Global Instability | Global conflicts, like the Ukraine war, increase military need, but recruitment struggles persist. |
Branch-Specific Analysis

Each branch of the US military has its challenges and trends in 2025. The Army, which is the largest branch with 443,000 active-duty personnel, has been hit hardest by recruitment issues.
The Space Force, by contrast, represents the newest and smallest branch of the military, with around 9,370 personnel.
Created to address the growing importance of space in national security, the Space Force has met its recruitment goals, reflecting its appeal to technologically inclined individuals and its unique role in protecting US interests in space.
Despite its small size, the Space Force plays a crucial role in the modern military landscape.
The Coast Guard, with 40,400 personnel, operates primarily under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime.
However, it can be transferred to the Department of Defense during times of war. The Coast Guard remains essential for protecting the US coastline and conducting maritime operations.
Overall, while each branch faces different challenges, the military’s recruitment crisis remains a common theme.
Demographic Changes in the US Military
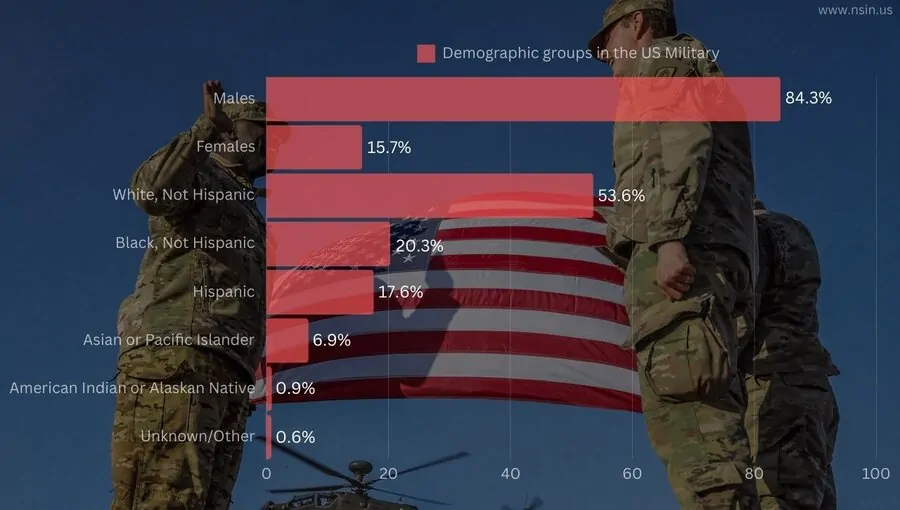
The demographics of the US military have shifted considerably in 2025.
One of the most notable changes is increased diversity within the ranks.
Approximately 31.2% of active-duty personnel are from racial minority groups, a figure that exceeds the 24.5% minority share of the general US population.
An increasing diversity reflects broader societal changes and the military’s efforts to recruit from all population segments.
The role of women in the military has also grown, with women now constituting 17.5% of the active-duty force. While women remain underrepresented in combat roles, their presence in leadership positions and support roles continues to expand.
The shift toward greater gender inclusion mirrors similar trends in other sectors of American society.
Age is another significant demographic factor, with the average age of active-duty personnel in 2025 being 28.5 years old, according to Usni.org.
However, this figure varies widely between branches, with younger service members typically found in the Army and Marine Corps, while older personnel are more prevalent in the Air Force, helicopter and aircraft crews, and the Navy.
These demographic changes have important implications for the future of the military, influencing everything from training protocols to health care needs.
Interesting Fact: The largest US military base outside the country is Camp Humphreys, in South Korea.
Health and Veteran Issues
@yolobrimgohard “Combat veterans may face mental health challenges such as PTSD, depression, and anxiety. Seeking help for these concerns is a sign of strength, not weakness. Let’s end the stigma and encourage open conversations about mental health in the military community. If you or someone you know needs support, please reach out. Resources are available. #mentalhealthawareness #veteransupport #endthestigma #mentalhealthmatters ♬ original sound – YOLO BRIM
The health and well-being of military personnel remain pressing concerns in 2025.
Many service members face long-term health risks related to combat experiences, including physical injuries and mental health challenges such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Toxic exposures, such as those from burn pits used in Iraq and Afghanistan, have created lasting health issues for thousands of veterans.
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) plays a central role in addressing these health concerns.
The VA provides medical care, rehabilitation services, and compensation to veterans who have sustained injuries or illnesses during their service.
In recent years, the VA has increased its efforts to address the needs of veterans who were exposed to harmful substances, such as radiation or chemical agents, during their time in the military.
Despite these efforts, many veterans continue to struggle with accessing the care they need, and the long-term health consequences of military service remain a significant issue.
Methodology
Data on the size, composition, and trends of the US military in 2025 were collected from multiple reputable sources to ensure accuracy and comprehensiveness. Primary sources included official reports from the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD), Congressional Research Service (CRS), and the Center for International Force Research (CIFR).
These provided the core statistics on active-duty personnel, reservists, and civilian employees. Demographic and recruitment data were also sourced from reports by the U.S. Naval Institute (USNI) and think tanks such as the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS).
Secondary sources, including news outlets and academic publications, were used to contextualize data on recruitment challenges and demographic shifts.
Articles from Fox News and The New York Times offered insights into economic and social factors influencing recruitment, while research from institutions like the Rand Corporation provided additional analysis on the role of technological advancements.
The data collection process involved compiling personnel numbers from multiple sources and verifying them through cross-referencing.
Summary
In 2025, the US military is smaller than it has been in decades, facing recruitment challenges and demographic shifts.
Global security challenges demand that the US maintain a capable and effective force.
Balancing these needs with modern-day realities will be key to ensuring the military’s ongoing role as a global power.
Sources
- DMDC – DoD Personnel, Workforce Reports & Publications
- Visual Capitalist – The Number of Active Duty Troops in Each U.S. State
- cnic.navy.mil – Naval Base Kitsap
- Milvets – Military Bases in North Carolina
- My Base Guide – Big Change for the Army’s Biggest Base
- WarfareHistoryNetwork – U.S. Involvement in WWII: How (and How Much) the Military Grew
- FoxNews – Military experts blame Biden’s DEI push as US military enters 2024 with smallest fighting force in 80 years
- TheNationalDesk – Army on track to hit recruiting goal with lowered target after shortfalls last 2 years
- ArmyuPress – Making Military Service Relevant to Gen Z
- CNN – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- SpaceNews – Space Force flexes muscle as Pentagon’s smallest but vital branch
- Department of Homeland Security
- Statista – Countries with the highest military spending worldwide in 2023
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs – PTSD: National Center for PTSD
Related Posts:
- What is an Average Military Nurse Salary in 2025?
- 5 Reasons Why Military Recruitment is Struggling in…
- How to Become a Military UAV Operator: A Complete…
- Who has the Best Military in the World in 2025 - Top 10
- The Ultimate Guide to Military Spouse Benefits in 2025
- How Many Generals Does the U.S. Military Have in 2025?







