The U.S. military, one of the largest in the world, plays an essential role in national defense and global stability.
With millions of personnel across various branches, the composition, recruitment, and demographic trends of the military have shifted in recent years.
Today, we shall go through the key aspects of the military’s current state, including size, gender, and racial representation, challenges in recruitment, educational attainment, age distribution, and the role of the National Guard and Reserves.
Without further ado, let us see how many people are in the us military and demographics.
1. Overall Size and Composition of the Military
How many people are in the US Military? The answer to that question is that, as of 2023, the U.S. military comprises approximately 2.87 million personnel, including both active-duty members and reservists.
According to the Congressional Research Service, the current composition is:
| Service | House-passed H.R. 8070 | FY2025 President’s Budget Request | FY2024 Enacted | Change from FY24-FY25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Army | 442,300 | 442,300 | 445,000 | -2,700 |
| Navy | 332,300 | 332,300 | 337,800 | -5,500 |
| Marine Corps | 172,300 | 172,300 | 172,300 | 0 |
| Air Force | 320,000 | 320,000 | 320,000 | 0 |
| Space Force | 9,800 | 9,800 | 9,400 | 400 |
| Total | 1,276,700 | 1,276,700 | 1,284,500 | -7,800 |
The military’s overall size has fluctuated over time.
For example, during periods of major conflict, the number of personnel was significantly higher than today. For instance, during WWII the number of active personnel was 12,209,238.
While the current military force is robust, it is smaller compared to those historical highs, reflecting both the changing nature of warfare and budgetary adjustments over the years.
In addition to active-duty personnel, the National Guard and Reserve components offer a vital supplement to the core force, ensuring that the military can respond flexibly to global needs.
2. Gender Representation

In recent years, gender representation in the U.S. military has shown a steady upward trend. As of 2022, women made up 17.5% of the active-duty force, marking significant progress in the inclusion of women in military service.
That represents continued growth from previous decades, particularly since 2005 when efforts to integrate women into more roles accelerated.
Female representation varies across the different branches.
The Air Force leads in this regard, with women accounting for 19% of its personnel, while the Marine Corps has the lowest proportion, with just 8%.
Despite these differences, women have increasingly occupied both enlisted and officer ranks, demonstrating their growing role in leadership and operational roles within the military.
Continued efforts to enhance gender equality, including the lifting of combat restrictions on women back in 2013, reflect the modern nature of military service.
3. Racial and Age Demographics
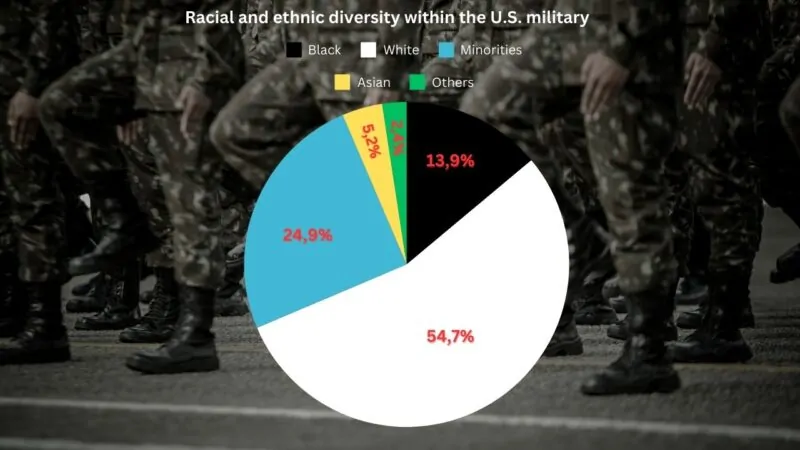
Racial and ethnic diversity within the U.S. military has long been a hallmark of its composition, and this trend has continued to grow in recent years.
- White – 68.8%
- Minorities – 31.2%
- Black – 17.3%
- Asian – 5.2%
- Others – 3.3%
- Multiracial – 3.1%
- Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander – 1.2%
- American Indian or Alaska Native – 1.1%
Diversity became vital for creating a military that represents the broader fabric of American society.
Within specific branches, there are notable trends in representation.
Meanwhile, Hispanic representation has been on the rise, particularly in the Marine Corps.
The growing ethnic diversity helps foster a more inclusive environment within the military, enriching the culture and offering broader perspectives in decision-making.
It also ensures that the military remains reflective of the society it protects.
In the same report by the MilitaryOnlineSource, the age distribution within the U.S. military reveals a young force with the average age of active-duty personnel being 28.5 years
- Marine Corps has the youngest average age, 25.3 years
- Space Force is the oldest, 31.4 years
Officers, due to their more extended careers and professional pathways, tend to be older than enlisted personnel.
The average age for officers is 34.5 years, reflecting their longer tenure and the greater time required to achieve leadership positions.
The age distribution across the branches and ranks contributes to a dynamic military structure, with younger service members executing physical tasks while more experienced personnel guide strategic decisions.
4. Recruitment and Retention Challenges

The U.S. military has faced significant recruitment and retention challenges in recent years.
In 2023, the military fell short of its recruitment goals by 41,000, a significant gap that has prompted concern among defense leaders.
Several factors have contributed to this issue, including a strong economy, which reduces the incentive for young people to seek military service, and a general decline in trust in institutions, especially among younger generations.
Demographic trends, particularly among Generation Z, have further complicated recruitment efforts.
What is even more important is to say that around 77% of the younger generation is unfit to serve in the army.
A shrinking pool of eligible candidates means that the military must work harder to attract and retain qualified individuals.
- Health
- Education
- Legal barriers
This has prompted the military to explore new strategies, including targeted recruitment campaigns and incentives, to bolster its ranks.
However, the challenge remains substantial and has broad implications for national defense.
Interesting Fact: In 2024, public confidence levels in the US armed forces were at 61%, according to Statista.
5. Educational Attainment in the Military
Education plays a key role in shaping the structure and career pathways within the U.S. military.
Officers typically have higher educational qualifications than enlisted personnel, a trend that reflects their leadership and management responsibilities.
Over 80% of military officers possess at least a bachelor’s degree, highlighting the emphasis on higher education for those in command positions.
The majority of enlisted personnel hold a high school diploma or have completed some college education.
Approximately 93% of enlisted members fall into this category, underscoring a notable educational disparity between enlisted personnel and officers.
The gap highlights the military’s hierarchical structure, where formal education often correlates with rank and responsibility.
While enlisted members can advance through various professional development programs, officers’ educational backgrounds remain a defining feature of military leadership.
6. Role of National Guard and Reserves
The National Guard and Reserves play a crucial role in supporting the active-duty military, providing a critical reserve force that can be mobilized when needed.
767,238 members were serving in the National Guard and Reserves, reflecting their importance in national defense.
These forces are unique in that they serve both federal and state governments, allowing them to respond to domestic emergencies and international conflicts.
In recent years, the role of the National Guard and Reserves has expanded, particularly during periods of extended conflict.
These forces have increasingly been deployed alongside active-duty units, demonstrating their integration into the broader military strategy.
The ability of the National Guard and Reserves to supplement the active-duty force ensures that the U.S. military can respond effectively to diverse challenges, both at home and abroad.
Methodology
The methodology used to gather data for this report involved a combination of quantitative and qualitative research approaches.
First, official government and military sources were analyzed, including reports from the U.S. Department of Defense, statistical data from military agencies, and resources such as Statista and MilitaryOnlineSource, which provided insights into the overall size, composition, and demographic trends of the military.
Secondary sources, such as articles and reports from reliable media outlets like Al-Jazeera, were used to supplement the statistical data and offer broader context, particularly regarding the presence of U.S. military bases worldwide.
Recruitment and retention challenges were examined through publicly available recruitment data and official reports that discuss shortfalls and factors influencing military enlistment rates.
To ensure accuracy in demographic and educational data, existing studies on military personnel, as well as official demographic reports, were consulted. The role of the National Guard and Reserves was researched through reports detailing their composition and deployment patterns, ensuring that the information reflects their dual federal and state responsibilities.
The Bottom Line
Now that we know how many people are in the US military and what are the demographics behind it, it is much easier to understand the composition.
The U.S. military, with its diverse and evolving composition, remains a vital force for national security.
While the army currently goes through recruitment challenges, demographic shifts, and the integration of women and minorities, it continues to adapt to the changing needs of the country.
The role of the National Guard and Reserves further strengthens its capabilities, ensuring a robust and flexible military presence.
Sources
- CRS Reports – FY2025 NDAA: Active Component EndStrength
- Nationalww2Museum – Research Starters: US Military by the Numbers
- US Department of Defense – Decline in Armed Forces Population While Percentage of Military Women Rises Slightly
- Air Force – Women’s legacy parallels Air Force history
- History – U.S. Military Lifts Ban on Women in Combat
- Al-Jazeera – Infographic: US military presence around the world
- MilitaryoneSource – 2022 Demographics Profile
- Work Chron – What Is the Average Age That Soldiers Join the Military?
- AirForceTimes – Air Force recruiting rebounds while Army, Navy still struggle
- Military – Even More Young Americans Are Unfit to Serve, a New Study Finds
- Army.mil – US Army launches first campaign spotlighting Army civilian careers
- Statista – Public confidence levels in the United States armed forces from 1975 to 2024
- TaskandPurpose – It’s 2017. The Military Still Requires Officers To Have College Degrees. Why?
- Prhome Defense – Characteristics of Active Component Accessions Education
- Gao.gov – Observations on Recent National Guard Use in Overseas and Homeland Missions and Future Challenges
- UsaFacts – How many people are in the US military?
Related Posts:
- How to Become a War Correspondent - Essential Tips…
- How Many Immigrants Came to the US in 2024? - What to Know
- A Look at US Military Helicopters: Past, Present, and Future
- The Rise of Ruggedized Displays - How ViewPoint…
- How to Structure a 12-Week Military Running Program…
- How Old Can a Woman be to Join the Military? Joining…







